Unnatural changes in the cartilage and bones of the spine cause the development of the disease, which, according to the ICD-10 code, refers to the localization of M42 and is called thoracic osteochondrosis. The middle part of the spine is less stressed than the lumbar and cervical spine, but deformities are difficult to heal. The load is unevenly distributed due to the rounded configuration of the sternum, osteophytes and other dysplastic manifestations appear.
Symptoms and signs
The disease occurs in the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc, spreads to the fibrous ring and other parts of the spinal segment that ensure the mobility of the spine. Changes manifest themselves in compression, reflex, or mixed neurological disorders and syndromes.
Pain is noticeable during physical exertion. There are different types of sensations:
- mild persistent pain in the chest is called dorsalgia;
- sharp and sharp colic, provoking difficult inhalation or exhalation, which leads to the immobility of muscles - dorsago.
Symptoms and treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine depend on the degree of wear and tear of the bone apparatus and the stage of aging, which are generalized and local.
Symptoms include:
- damage to the peripheral processes of the nerves (neuralgia), characterized by painful attacks along the intercostal vasoconstrictors;
- Concentration of pain in the left side of the chest or the appearance of a severe painful feeling like shingles;
- decreased mobility of the spine in the chest area;
- Numbness in arms and hands;
- decreased sexual function;
- the appearance of pain in the area of internal organs can cause the heart, stomach, liver;
- Lumbago in the neck, cheekbones and head, cough or a lump in the throat;
- Arrhythmia, tachycardia, fever.
Signs of osteochondrosis are disguised as manifestations of related diseases, so symptoms are ambiguous. Spinal nerves are concentrated around the spine; when pinched, signals are sent to different parts of the body and organs.
Causes of Osteochondrosis
There is no precise information about what factors deform the intervertebral discs. A common reason for osteochondrosis is scoliosis, or curvature of the spine, which is more commonly seen in children and adolescents.
The theory takes into account such factors of vertebral deformity:
- dysontogenetic;
- hormonal;
- vascular;
- functional;
- involutive;
- contagious;
- immune;
- dysmetabolic;
- mechanically;
- hereditary.
The deterioration and aging of bones and cartilage occurs as a result of previous exposure to adverse conditions. Atrophic degenerations in the spine are predetermined by a genetic factor, and a disease with clinical symptoms arises under the influence of an exogenous and endogenous environment.
The consequence in the form of complications in the work of the vertebrae occurs when the process of destruction of complex substances outweighs their synthesis. Worsening occurs when the hard drive has lost power and lacks useful elements. The penetration of elements and dissimilation products decreases, the viability of the cells decreases and parts of the cells accumulate through self-destruction. The production of complex proteins is reduced, collagen fibers are destroyed.
The mechanical effect on the ring-shaped connective structure increases, the layer structure is disorganized, and the fiber skeleton is torn. The intervertebral disc is squeezed under the influence of biomechanical factors and body movements and its ability to fixate decreases. A decrease in hydrostatic pressure allows blood vessels and nerves to grow into the annulus.
Diagnostic methods
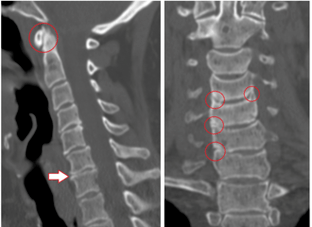
The detection identifies radicular, pain, reflex, myotonic, autonomic, and vascular factors. The best method of examination is difficult to determine, since the diagnosis is made individually in each case.
The main methods are:
- X-ray diagnostics;
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
X-rays analyze the condition of the spine, images are given in oblique, side and direct projection. Sometimes a person bends, bends, or leans to one side for a photo.
Contrast radiography is divided into the following studies:
- Pneumomyelography - 20 to 40 ml of air is injected into the spinal canal;
- Angiography - 10 ml of contrast medium is injected into the vertebral lumen and 7 to 9 images are taken in 2-3 seconds;
- Myelography - an injection of a colored liquid is carried out into the subarachnoid lumen, followed by fluoroscopy of the structure;
- Discography - the colored substance is injected directly into the intervertebral disc for localized examination.
Computed tomography evaluates the structure of bones and tissues and the condition of the blood vessels. The painless method takes three-dimensional images in a few minutes.
Advantages of CT:
- high recognition speed;
- Screening of "stupid" areas during diagnostics on the move;
- the possibility of multispiral angiography;
- Detection of long objects with high quality, thin cuts.
MRI uses the magnetic field of a machine that builds hydrogen atoms in the human body in parallel with the action. The particle signal, the reaction is recorded. The tomograph recognizes the waves and shows the result on the screen. There is no radiation in MRI, the method is less dangerous but is not recommended for pregnant women.
Treatment and prevention
It is necessary to treat osteochondrosis in several stages, the complexity depends on the severity of the disease, contraindications and body resources.
Methods:
- Drugs and medication;
- Methods of physiotherapy, exercises for removing braces, alleviating the patient's condition;
- Operation.
There is a direction of exercise therapy, within which it is possible to cure problems of the spine in the form of a hernia, spondylosis with rehabilitation gymnastics. A method of recovery from surgery has also been developed.
Yoga exercises help adult men, women, a child to overcome pain, warn that the main thing is a psychological attitude.
Medication
Medications are prescribed by a neurosurgeon or neuropathologist according to the map and medical history. Patients take drugs in the hospital or at home, the main thing is that they follow the instructions and do not deviate from the intake schedule.
Common medications:
- NSAIDs relieve pain, fever, and inflammation;
- Muscle relaxants lower the muscle tone of the skeletal skeleton;
- Hormones reduce neuralgic pain;
- Vitamins B2, B6, B12, A and C are taken during remission and for simple prophylaxis;
- Diuretics relieve swelling and loosen pinched root nerves;
- neurometabolic stimulants improve metabolism in nerve tissue;
- Chondroprotectors restore the cartilage of the vertebrae after damage.
Sometimes at the first stage of the appearance of unpleasant sensations, the patient refrains from using drugs. It is enough to move, use a massager.
physical therapy

This type of exposure is used in conjunction with drug treatment or separately. In addition, bed rest is applied, heat is applied to the affected area. Folk recipes are used to relieve pain.
Physiotherapy in a medical facility includes procedures:
- Ultrasound and phonophoresis;
- Shock wave therapy;
- Detensor impact;
- Laser therapy;
- Electrotherapy;
- magnetic waves;
- Mud therapy and balneotherapy;
- Massage.
Ultrasound involves the action of high frequency waves on the tissue, which reduces sensitivity to pain. Ultraphonophoresis involves adding pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs to better reach the affected areas.
Shock wave therapy is the transmission of an acoustic wave to the painful area, it is used to improve blood circulation and speed up metabolism. Detensor therapy consists of stretching the spine with the patient's body weight.
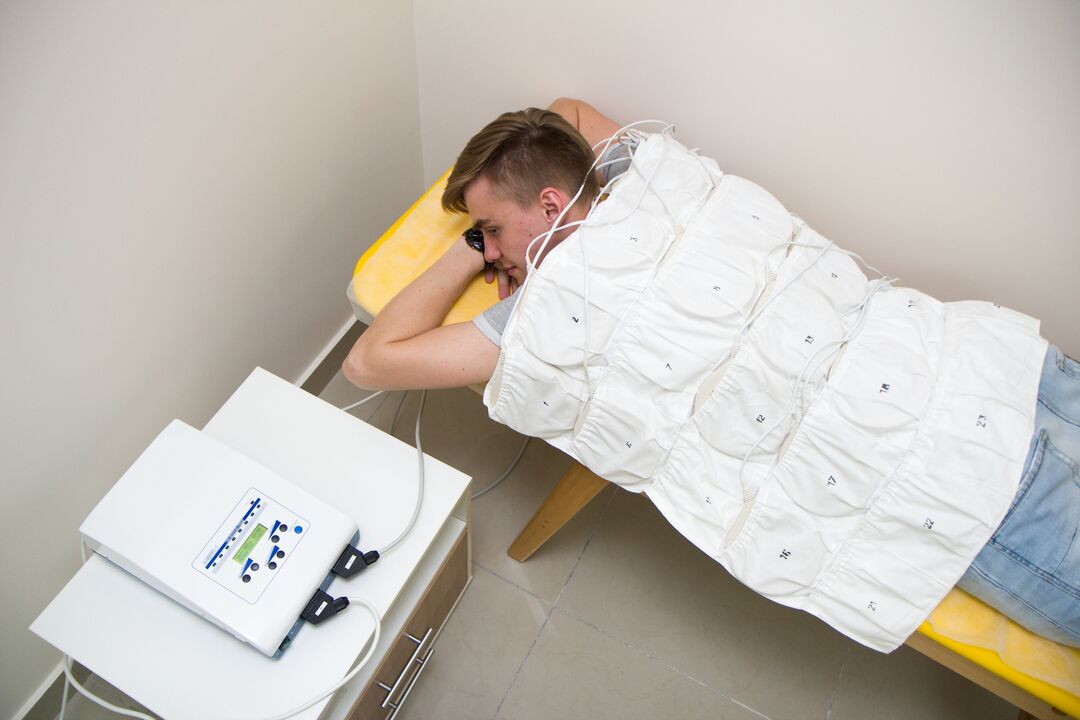

Laser therapy is based on the helium-neon generation of lasers to activate bioelectrical currents in nerve fibers. The laser acts on inflamed nerve roots in the paravertebral area along the thoracic spine.
Electrotherapy improves the nutrition and metabolism of products in tissues, and impulse currents affect the sensory nerve endings. Low-frequency waves relieve acute pain and serve as first aid.
Magnetic therapy is used to relieve swelling, cramping, and inflammation. A magnetic wave inductor is placed on the affected chest region. Balneo and mud therapy consists of swimming in swimming pools, bathing, alternating showers for treatment and during relaxation. The metabolism is normalized, the blood flow to the affected areas is accelerated, pain and inflammation are reduced.
Therapeutic massage for osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is vacuum, point and lymphatic drainage, improves blood microcirculation, nourishes tissues and tightens muscles. The sessions are carried out by a competent specialist. Entrusting the spine to laypeople can lead to dangerous consequences. Massage is prescribed after the end of the acute stage, the first session should not exceed 10 minutes.
Operative treatment
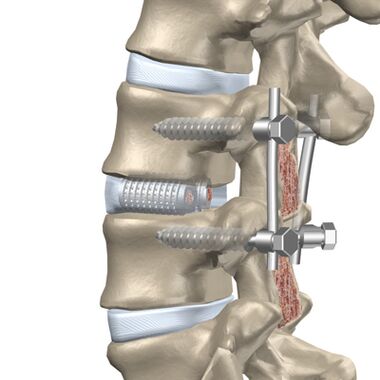
The patient is indicated for surgery if medical treatments, massages, and other measures do not alleviate the condition.
The intervention is divided into 2 phases:
- Eliminating the cause of severe pain (decompensation);
- Stabilization of the spine.
A facetomy is performed for the posterior approach because facet joints can press on nerves. Foraminotomy is the widening of the root canal through which the nerve leaves the vertebra. A laminectomy involves removing the back part of the vertebra that protects the lumen of the spine and, due to the deformity, presses on the brain. Laminotomy involves widening the opening of the canal that contains the spinal cord while removing a separate fragment of the posterior vertebral area.
Anterior operations are performed when there is a protrusion (protrusion of the disc toward the spinal lumen) or a hernia toward the canal.
The following methods are used for front decompression:
- Discectomy - removal of an entire disc or a separate part of it;
- Corpectomy - removal of an entire vertebra and the adjacent disc, followed by implantation.
Discectomy and corpectomy lead to a destabilization of the column and increase the risk of neurological defects. Rigid fixation or fusion of three vertebrae (fusion) is used.
Prevention of breast osteochondrosis

Exacerbations of the disease reduce the working capacity and quality of life of the person, therefore special attention is paid to prevention. As a result, vertebral degeneration occurs later and obstruction is avoided.
Methods of preventing the disease:
- Decrease in physical activity on the spine;
- You can not stand still for a long time without changing the support member, you can lean against an improvised object or wall;
- sitting at a desk for long periods of time is not recommended, and when using a computer you need to take active breaks, walk around.
- Mattresses and orthopedic headrests are chosen for sleeping;
- when running and walking you need to avoid sudden turns and jumps, walk in shock-absorbing shoes with small heels.
- Carrying weights no more than 10 kg, gradually raise them from a sitting position.
In the car, you need to use cushions for the back and headrests, while the driver's seat needs to be rigid. Work cannot be carried out in a half-sloping position, you can stand or sit. Well-developed muscles support the skeleton, so pay attention to practicable sports training and hardening.
Possible complications
The disease develops for a long time, sometimes the symptoms of pain do not appear immediately. All degenerative changes in the chest area lead to the appearance of pathologies.
Types of complications:
- pathology of the heart vessels with subsequent myocardial infarction or angina pectoris;
- Intercostal neuralgia, or inflammation of the peripheral nerves with chest pain from root compression;
- Bulging of the intervertebral discs.
Complications occur with advanced forms of osteochondrosis, so timely treatment in the early stages helps to avoid comorbidities.



























